Hypothermia develops if the body temperature drops below 95 degrees F. Remember that significant complications might arise from this drop in the temperature including death. The condition is considered dangerous since it affects the ability of the individual to think clearly.
Cold weather is the main cause of hypothermia. Once the body is subjected to extremely cold temperatures, it rapidly loses more heat than what is being produced. If the body could not produce enough heat, the body temperature will rapidly drop.
Indications
- Slowed breathing
- Excessive shivering
- Stumbling
If the individual has a weak pulse, excessive fatigue or loses consciousness, he/she might be suffering from hypothermia. - Slowed speech
- Clumsiness
- Confusion
If the individual has a weak pulse, excessive fatigue or loses consciousness, he/she might be suffering from hypothermia.
Risk factors
- Age – infants and the elderly face the highest risk due to diminished ability to control the body temperature
- Mental illness and dementia – these conditions put one at higher risk
- Alcohol and drug use – both can impair judgment about the cold and one is likely to lose consciousness
- Other medical conditions – some conditions can disrupt the ability of the body to maintain adequate temperature or feel cold such as arthritis, hypothyroidism, diabetes, dehydration and Parkinson’s disease.
- Certain medications – some sedatives, antidepressants and antipsychotic drugs can disrupt the ability of the body to control temperature.
Management
Hypothermia is considered as a medical emergency. Call for emergency assistance if an individual is suspected with hypothermia.
The objective of treatment is to increase the body temperature to a normal range. While waiting for the medical team to arrive, the following should be considered:
- Proper handling of the individual – make sure that the individual is handled carefully and transferred to an area away from the cold. Do not attempt to massage to restore the flow of blood. Remember that any excessive or forceful movements can lead to cardiac arrest.
- Get rid of wet clothing – remove soiled or wet clothing and cover the individual with warm blankets. If a blanket is not available, use body heat to warm the individual. If conscious, provide a warm beverage or soup to increase the body temperature.
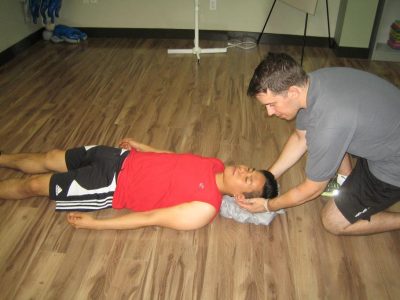
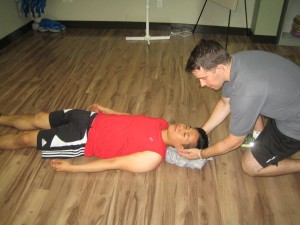
- Apply a warm compress – the compresses should be applied to the chest, neck or groin.
- Monitor the breathing – if the breathing of the individual is slow or loses consciousness, perform CPR if trained to do so.
Medical care
In severe cases of hypothermia, it is treated medically with warm fluids, often saline which is injected into the veins. The doctor rewarms the blood with a procedure where blood is drawn, warmed and placed back into the body.
Airway rewarming can be done via nasal tubes and masks. Warming the stomach using a cavity lavage or stomach pump where a warm saltwater solution is pumped into the stomach can also help.
More Information / Disclaimer
The information posted on this page on hypothermia is for learning purposes only. Learn to recognize and manage cold-related ailments by taking a standard first aid course with Red Deer First Aid.